Maximizing SSD Performance with SLC Cache
1/4/2567
Maximizing SSD Performance with SLC Cache
Some SSDs, previously much faster, now exhibit significantly diminished performance. Speed testing software inspection may discover a halving of write speed. This predicament impacts numerous customers, sparking a surge in FAE engagement with the manufacturer to ascertain whether it signals SSD failure or stems from subpar manufacturing quality. After manufacturer consultation, it turns out that the experienced performance slump resulted from a full individual SLC cache, which will necessitate cache clearance to reinstate the SSD's prior performance level.
What is SLC Cache?
SLC is a type of NAND flash memory where each storage unit stores only one bit of data. Compared to other types of flash memory, it performs the simplest operations, resulting in faster data writing, lower power consumption, and higher durability. However, its main drawback is lower density and higher cost per gigabyte of flash memory.
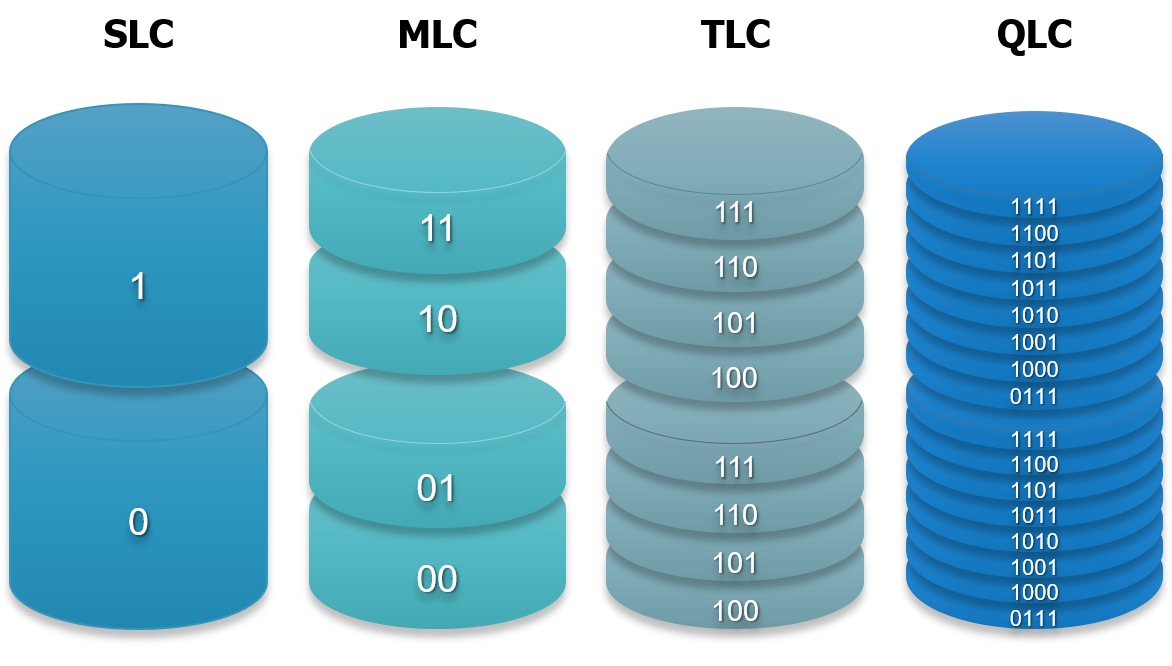
On the other hand, SSDs based on 3D TLC have lower cost per gigabyte and can store more data, but they may suffer from slower read/write performance because each storage unit stores three bits of data. This slowdown is most noticeable in SSDs without DRAM cache.
To address this issue, SSD vendors reserve a portion of the SSD and utilize it as cache. This portion, called "SLC cache”, simulates the SLC SSD's read/write performance by storing only one bit of data.
SLC Cache Types
Static Cache
Dynamic Cache
Conclusion
SLC caching is a sophisticated technique used for write caching on SSDs. It enables high transfer speeds for writes, even reaching hundreds of gigabytes on flash memory that typically cannot sustain such speeds. Data written to the cache is swiftly transferred to the TLC or QLC flash memory to ensure the cache is available for peak transfer speeds.
The size of the SLC cache differs based on the available free space on the drive. Consequently, larger and less occupied drives can write more data at peak speeds compared to smaller SSDs or those nearing full capacity.
So, the next time you encounter the same performance issues, don't jump to conclusions about SSD issues. Instead, check the SSD's capacity and see if there is any unnecessary data that can be trimmed first. This step may help to recover your missing performance.
