-
Productos
Embedded Computing
- AIoT Software, Distribution & Services
- Application Focus Embedded Solutions
- Arm-Based Computing Platforms
- Computer On Modules
- Digital Signage Players
- Edge AI & Intelligence Solutions
- Embedded PCs
- Embedded Single Board Computers
- Fanless Embedded Computers
- Gaming Platform Solutions
- Industrial Display Systems
- Industrial Flash & Memory Solutions
- Industrial Motherboards
- Industrial Wireless Solutions
- Wireless ePaper Display Solutions
Cloud, Networking & Servers
- Industrial, Telecom and Cloud Servers
- Network Interface & Acceleration Cards
- Network Security Appliances
- SD-WAN & uCPE Platforms
- WISE-STACK Private Cloud
Applied Computing (Design & Manufacturing Service)
Industrial Automation & I/O
- Automation Controllers & I/O
- Certified Solutions
- Class I, Division 2 (CID2) & ATEX Solutions
- Data Acquisition (DAQ)
- Embedded Automation Computers
- Gateways & Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
- Human Machine Interfaces
- Panel PC
- Power & Energy
- Remote I/O
- WebAccess Software & Edge SRP
- Wireless I/O & Sensors
Intelligent Connectivity
- Cellular Routers and Gateways
- Ethernet / Serial Device Servers
- Industrial Ethernet Switches
- Industrial Media Converters
- Industrial Protocol Gateways
- Industrial Wireless and Gateways
- Intelligent Connectivity Software
- Serial / USB Communications
Computer Vision & Video Solution
- Advanced Video Appliances
- Edge AI Jetson Platforms
- Intelligent Vision Camera & Software
- Video & Vision Cards
Intelligent Systems
Intelligent Healthcare
- Carros de Enfermería Computarizados
- Computadoras Médicas
- Pantallas Médicas
- Sistemas Inteligentes de Energía
- Terminales de Info-Entretenimiento para Cuidado de
Intelligent Mobile Solutions & Logistics
- Environmental Sensing & Cold Chain Solutions
- Industrial Tablets
- Rugged & In-Vehicle Edge AI Solutions
Intelligent City Services & Retail
- All-in-One Touch Computers & Kiosks
- iCity Service & iRetail Solution
- POS & Tablets
- Signage & Edge Computers
Industrial Mounting (Stands/Arms/Workstations)
- Soluciones
- Servicios
-
Socios
Business Alliance Partner
- Soporte
- Corporativo
- Contactarnos
Registro de MyAdvantech
MyAdvantech es un portal personalizado para clientes de Advantech. Al registrarse como un miembro de Advantech, puede recibir las últimas noticias sobre productos, webinar y ofertas especiales en eStore.
Inscríbase hoy para obtener acceso rápido a la información de su cuenta.
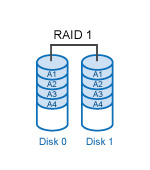
What is RAID?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that allows multiple hard drives to be combined into a single storage unit. Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways or RAID levels," depending on the level of redundancy and performance required. RAID levels are not ratings, but rather classifications of functionality. Different RAID levels offer dramatic differences in performance, data availability, and data integrity depending on the specific I/O environment. There is no single RAID level that is perfect for all users.
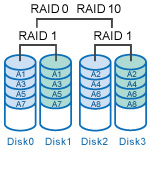
RAID Type and Application
There are number of things that need to be considered when choosing a RAID solution:
- Performance and Application Requirements:Read and write performance, failure tolerance, and data redundancy are the main factors to consider when selecting the right RAID solution for your application. (See Table 1)
- Hard Disk Drive Capacity and RAID Card Scalability:Some RAID cards can connect up to 256 SAS/SATA hard drives while others can only connect to 4. The number of HDDs to be used in a RAID solution and how much disk space needed for future storage are two main decision points to consider in selecting RAID card.
- Cache Protection:Cache protection protects cache memory on the RAID card by using an additional battery pack. Only certain RAID cards support cache protection. For companies that cannot afford data loss due to a power outage, cache protection on the RAID card is a must.
- Cost Concern:Cost is always associated with performance. For some corporations, performance is a bigger concern than cost. But when cost is a concern, learning to balance cost vs. performance during implementation of a RAID solution, will be very critical.
Table 1
RAID Selection
- Entry Level
- Best Value
- High Performance and Reliability
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||